Query Records
This node is used to fetch a selection of records from the Noodl Cloud Services backend. You can provide a query to define the selection of records you want to retrieve.
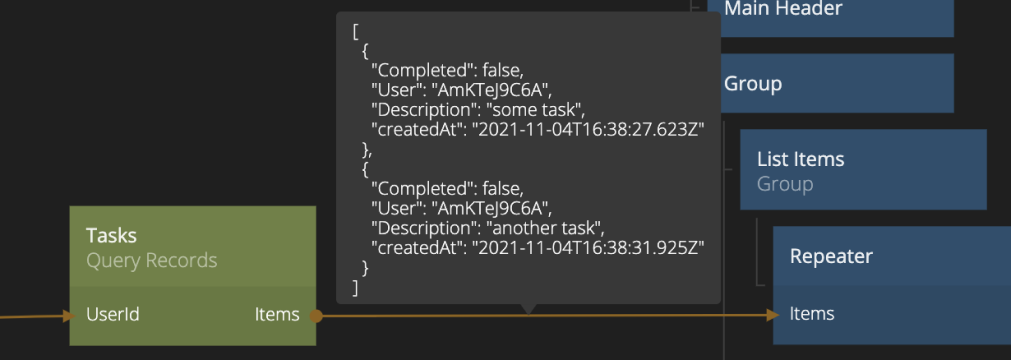
You can specify the query using filter, sorting and limit in the Property Panel.
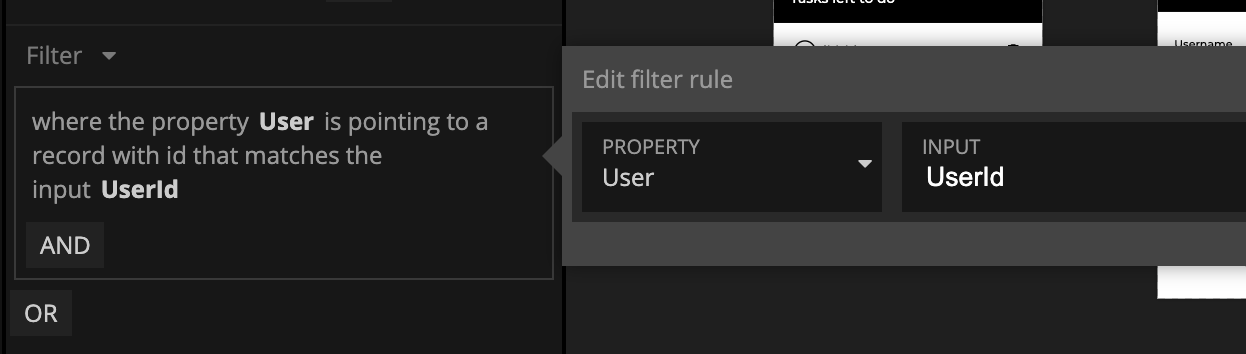
Filters
By default the Query Records will fetch all Records, you can however add a filter. You can choose from a simple filter where you can filter on one or more Record properties, or a more advanced JSON based filter syntax, that also can include Javascript logic.
Simple Filters
The Simple filters are created through a UI where you select properties and how to filter them in the filter panel.

Note that you can select if you want the filter to use a static value or a value that comes from an input.
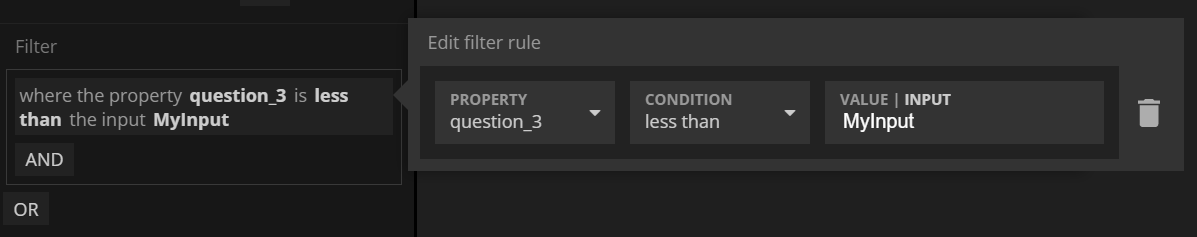
Sorting with Simple Filters
By default the Query Records does not return the result of a fetch sorted. You can specify sorting. Like filters you add which properties you want to sort on.
For each property you can choose the sorting order.

Limit
Be default up to a 1000 records are returned. But you can specify a Limit, the number of records to return, and Skip, at what index to start returning records. This is very useful for pagination when listing records.
Total Count
If you choose to limit the returned records or if you have more than the maximum allowed return records you can request the total count to be returned with your query.
By enabling this you will provide the total count on the Total Count output.
Advanced filters
If you choose Advanced as filter type you will get the option to specify a filter script. This is regular javascript code but you need to end the script by calling the where function with the filter definition provided. This is done using the following syntax:
where({
Completed: { equalTo: true },
});
The above filter will return all Records in the collection that has the Completed property true. You can select from a number of operators:
- lessThan Less Than
- lessThanOrEqualTo Less Than Or Equal To
- greaterThan Greater Than
- greaterThanOrEqualTo Greater Than Or Equal To
- equalTo Not Equal To
- notEqualTo Not Equal To
- containedIn Contained In
- notContainedIn Not Contained in
- exists A value is set for the key
- matchesRegex Check if a value matches a regex pattern
- text Text search in one or several columns using a text index
- idEqualTo Match the id of the item to a specific id
- idContainedIn Check if the id of the item matches an id in an array of ids
- pointsTo Check if the id of the item matches an id in an array of ids
- relatedTo Checks if the item is related to another item, through a relation
For instance, to filter on if a certain property (in this example Letter) is one of many possible values:
where({
Letter: { containedIn: ["A", "B", "C"] },
});
Or to filter all Records that have a value set for a specific property:
where({
Letter: { exists: true },
});
You can also combine these filters into expressions using and and or, for instance:
where({
and: [{ ZipCode: { exists: true } }, { Score: { greaterThan: 10 } }],
});
You can also use the matchesRegex operator to filter by regular expression, this is generally slow and not recommended for large sets. Learn more here
where({
SomeString: { matchesRegex: "pattern", options: "i" },
});
As mentioned above the filter script is a javascript function so you can provide javascript code if you like:
where({
SomeDate: { equalTo: new Date() },
});
You can also specify variables instead of explicitly specifying the filter values, this will create an input port on the Query Collection node that can then be connected to. You specify variables simply by using the Inputs object. The filter below will create an input called MyStringInput.
where({
SomeString: { equalTo: Inputs.MyStringInput },
});
You can also do text search in strings. This will create an index in the database and text search only works on one property so you have to choose wisely. Also text search matches whole words and must be the first filter in an and or or sequence.
where({
SomeString: { text: { search: Inputs.MyStringInput } },
});
You can also toggle case sensitivity for text searches.
where({
SomeString: {
text: {
search: {
term: Inputs.MyStringInput,
caseSensitive: true,
},
},
},
});
If you need to match the Id of Records in the collection you need to use the special operation:
where({
idEqualTo: Inputs.TheRecordId,
});
In the above filter you can connect a Record Id output to the TheRecordId parameter to fetch just one specific object. You can also request a set of object based on their Id.
where({
idContainedIn: [Inputs.FirstObjectId, Inputs.SecondObjectId],
});
Some properties in your Records can be of Pointer type, that means that they reference another Records with a specific Id. If you want to filter out Records that point to a specific Records, use this syntax. Let's say you have a collection of Post Records, each have a set of Comment Records where each Comment points back to it's owning Post via the Owner property. The filter below will find all Comments for a Post given that you provide the post id.
where({
Owner: { pointsTo: Inputs.MyPostId },
});
You can also provide an array if you want to find Comments that are related to a set of Post Records.
where({
Owner: { pointsTo: [Inputs.MyFirstPostId, Inputs.MySecondPost] },
});
Don't forget that you need to send a signal to Fetch to perform a new fetch with a new filter if any of the filter inputs have changed.
Records also support many-to-many relationships via Relations. You can filter our all Records in the collection you are querying that are related to a specific Record via a Relation with a given key using:
where({
relatedTo: { id: Inputs.MyRecordWithARelation, key: "the-relation-key" },
});
Geo queries
Noodl allows you to associate real-world latitude and longitude coordinates with an object. Using a GeoPoint property type in a class allows queries to take into account the proximity of an object to a reference point. This allows you to easily do things like find out what user is closest to another user or which places are closest to a user.
If you have a Record with a GeoPoint type property called Location you can use these queries, first nearSphere, it will return results ordered by the distance from the specified latitude and longitude point.
where({
Location: {
nearSphere: {
latitude: 48.0,
longitude: -110.1,
},
},
});
You can also specify a maximum distance from the center point by using either maxDistanceInMiles or maxDistanceInKilometers, e.g.
where({
Location: {
nearSphere: {
latitude: 48.0,
longitude: -110.1,
maxDistanceInKilometers: 100,
},
},
});
Another option is to query only records with Location that are within a certain rectangular bounding box. This makes it possible to query for the set of records that are contained within a particular area. It's done using the withinBox query.
where({
Location: {
withinBox: [
{
latitude: 37.71,
longitude: -122.53,
},
{
latitude: 30.82,
longitude: -122.37,
},
],
},
});
It’s also possible to query for the set of records that are contained within or on the bounds of a polygon. Opened or closed paths are allowed, minimum of 3 points. It's done using the withinPolygon query.
where({
Location: {
withinPolygon: [
{
latitude: 25.774,
longitude: -80.19,
},
{
latitude: 18.466,
longitude: -66.118,
},
{
latitude: 32.321,
longitude: -64.757,
},
],
},
});
Sorting in advanced filters
To specify the sort order when using advanced filter you run a function called sort in the filter script.
where({
// You where filter here
});
sort(["createdAt"]);
The sort function takes an array with strings specifying the names of the properties you want to sort by. You can prefix the property name with "-" to specify that you want to sort in descending order instead of the default ascending order.
sort(["-Age", "createdAt"]);
Inputs
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| Class | Select the Class for the types of records this node should query. When the Class is selected you can create filters and sorting based on the properties of the Class. |
| Filter | This specifies the type of filter, you can choose from:Visual: Specify your filter using the visual filter editor.JavaScript: Specify your filter using JavaScript (this is more flexible and you can create more dynamic queyries but it's also more complex) |
| Use Limit | Enable or disable the use of limit, i.e. that you can specify how many records are returned as a maximum and if a number of record should be skipped. |
| Limit | The maximum number of records to be returned by the backend. |
| Skip | This property allows you to skip a number of records from being returned by the backend. Using Skip and Limit allows you to do paging, e.g. return records from 10-20. |
| Fetch Total Count | Enable this to also query for the total count of records matching the filters. Even if you limit the returned result. |
| Query Parameters | The input for specifying the value of a query parameter. Each paramteter used in your query will get an input where you can provide a value through a connection. |
| Signal | Description |
|---|---|
| Do | Send a signal here to perform the query and fetch matching records from the backend. |
Outputs
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| Items | The result of the query as an array of Records. |
| Count | The number of records in the result. |
| First Record Id | The Id of the first Record in the result array. |
| Error | This output contains the error message incase something when wrong when executing the query. |
| Total Count | If Fetch Total Count is enabled then this output will contain the total number of records that match the query. Even if you limit the returned result. |
| Signal | Description |
|---|---|
| Success | A signal is sent here if the query was successful and the result is ready. |
| Failure | A signal is sent here if something went wrong with the query. You can find the error message via the Error output. |